Using Packet Radio for Winlink
Sholto Fisher, K7TMGArticle from the West Mountain Radio Quarter 4, 2021 Newsletter
One of the frequent technical support issues I'm asked to help resolve is getting Winlink Express working on VHF with 1200 baud Packet Radio and a sound card interface.
The reoccurring factor I've noticed with these support calls is the user is usually unaware that Winlink Express cannot produce the Packet Radio audio waveforms itself. It must use a Packet Radio driver application to do this.
The following diagram shows how all the "moving parts" need to be connected in order for successful Winlink Packet Radio operation.
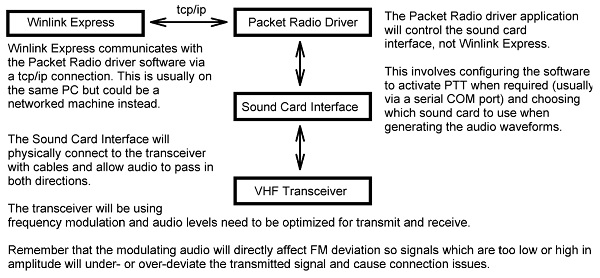
You have a choice of Packet Radio driver software to use with Winlink (e.g. UZ7HO, Dire Wolf, AGW PE). The UZ7HO software is free and highly recommended. See http://uz7.ho.ua/packetradio.htm
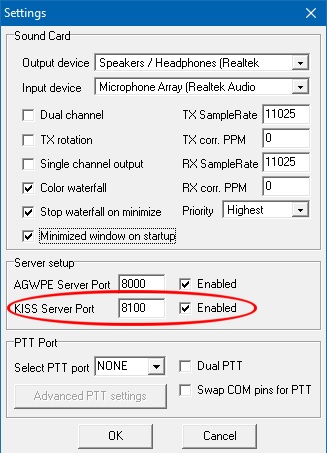
We don't need to configure much in UZ7HO Sound Modem as the Winlink Express software will set most parameters for us but we have to enable the KISS interface. This is in the settings screen and I've highlighted it in red.
Note that this is also where you configure which sound card to use, and the PTT method.
If no PTT port is chosen then operation would rely on the sound card interface's VOX circuit.
The next step is to tell Winlink Express to use it. We do this in the Packet Winlink/P2P Setup screen.
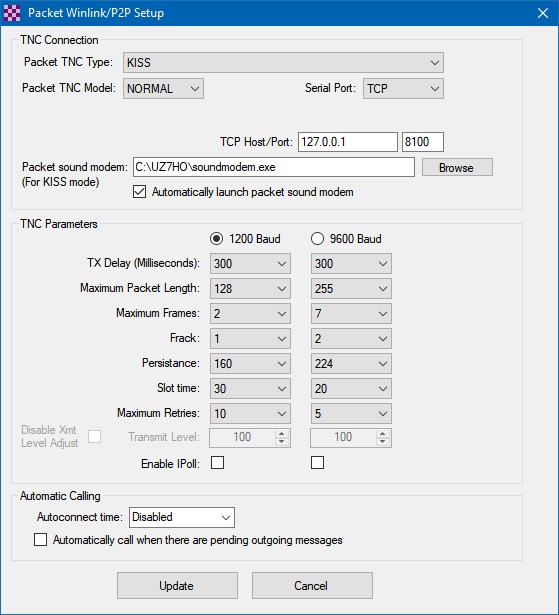
The Packet TNC Type should be set to KISS and the "Serial Port" will be TCP.
The TCP Host/Port refers to the PC running the UZ7HO Sound Modem application (usually the same computer so the localhost address of 127.0.0.1 and port 8100 is chosen).
If you specify the path to the Packet driver application and check the option then Winlink Express will automatically run Sound Modem when you open the Winlink session.
The TNC parameter defaults are often good enough to start with but there's some optimization which can be done depending on your local conditions.
Packet length (PACLEN) and Maximum Frames (MAXFRAME) can be reduced or increased depending on activity and distance to the RMS.
Packet Radio is a complex subject and further reading should be done if you want to understand how network parameters can affect traffic flow. Quite often your local ham club will have information on the correct parameters to use locally.
The final thing to configure is your sound card volume levels.
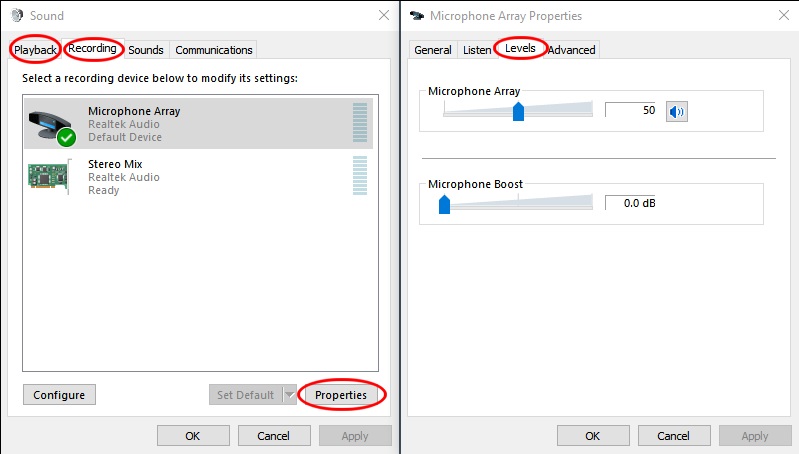
Experimentation may be necessary to find the "sweet spot" where FM deviation is optimal. 1200 Baud Packet Radio is not too fussy but deviation becomes critical at higher speeds (e.g. 9600).
On Windows 10 I find the easiest method to change both the Playback volume (TX audio) and Recording volume (RX audio) is from the Sound Control Panel.
You can create a shortcut on your desktop that points to mmsys.cpl for easy access. I suggest starting with values of 50% for both Playback and Recording and go from there.
Categories that this topic belongs to: RIGblasters

